Configure Site-to-Site Connectivity for APIs with mTLS
This guide provides step-by-step instructions for using ngrok for site-to-site connectivity. This example shows you how to securely run the ngrok agent at an external site to get access to locally running APIs. The connection will be end-to-end encrypted using mutual TLS (mTLS).
For a deeper understanding for how mTLS is implemented within ngrok, reference the Mutual TLS module page.
Ready to educate your customers with information about why they must install the ngrok agent to enable site-to-site connectivity, your shared options for architecture and security, and operational best practices? Send them to our end customer installation guide.
Prerequisites
A certificate authority (CA) is required for mTLS. The CA is responsible for issuing and digitally signing certificates (client certificates). The CA will also be used to verify the authenticity of the certificates.
- CA certificate to be used by ngrok to verify the clients.
- Client certificates signed by the CA used to access the endpoints.
Users are responsible for providing the CA and client certificates. ngrok will not generate them. The CA certificate will be uploaded and hosted on the ngrok platform. The client certificates will need to be distributed to any client/device that will need to access the API endpoints.
Most organizations will have their own certificate mangement infrastructure. You can generate test certificates for reference/demo purposes during implementation.
Install the ngrok agent
Download the appropriate version and install it on the same subnet as the APIs you want to access.
Get an ngrok API Key
Create an ngrok API key using the ngrok dashboard. Make sure you save the API key before you leave the screen because it won't be displayed again.
Configure a custom agent ingress address
Configuring a custom agent ingress address allows you to provide your customers with
a dedicated URL to connect to the ngrok platform. Since your customers will connect using your subdomain,
they can safely block other ngrok domains to control the tunnels started in their network. You'll provide a
subdomain you own, such as connect.{YOUR_DOMAIN}, and delegate DNS (Domain Name Service) control of
that subdomain to ngrok.
Create the agent ingress address
Use the ngrok API to create the custom agent address by running the command below, substituting your own values for the variables:
Loading…
You should receive a 201 response similar to the following:
Loading…
Save the values from the ns_targets property and the region_domains
property as you'll use them later.
Update your DNS�
Create an NS record in your DNS provider's registry for each ns_targets value from the
response above, using connect as the name for each entry. The screenshot is from AWS Route53, but
you can use any DNS provider you choose.
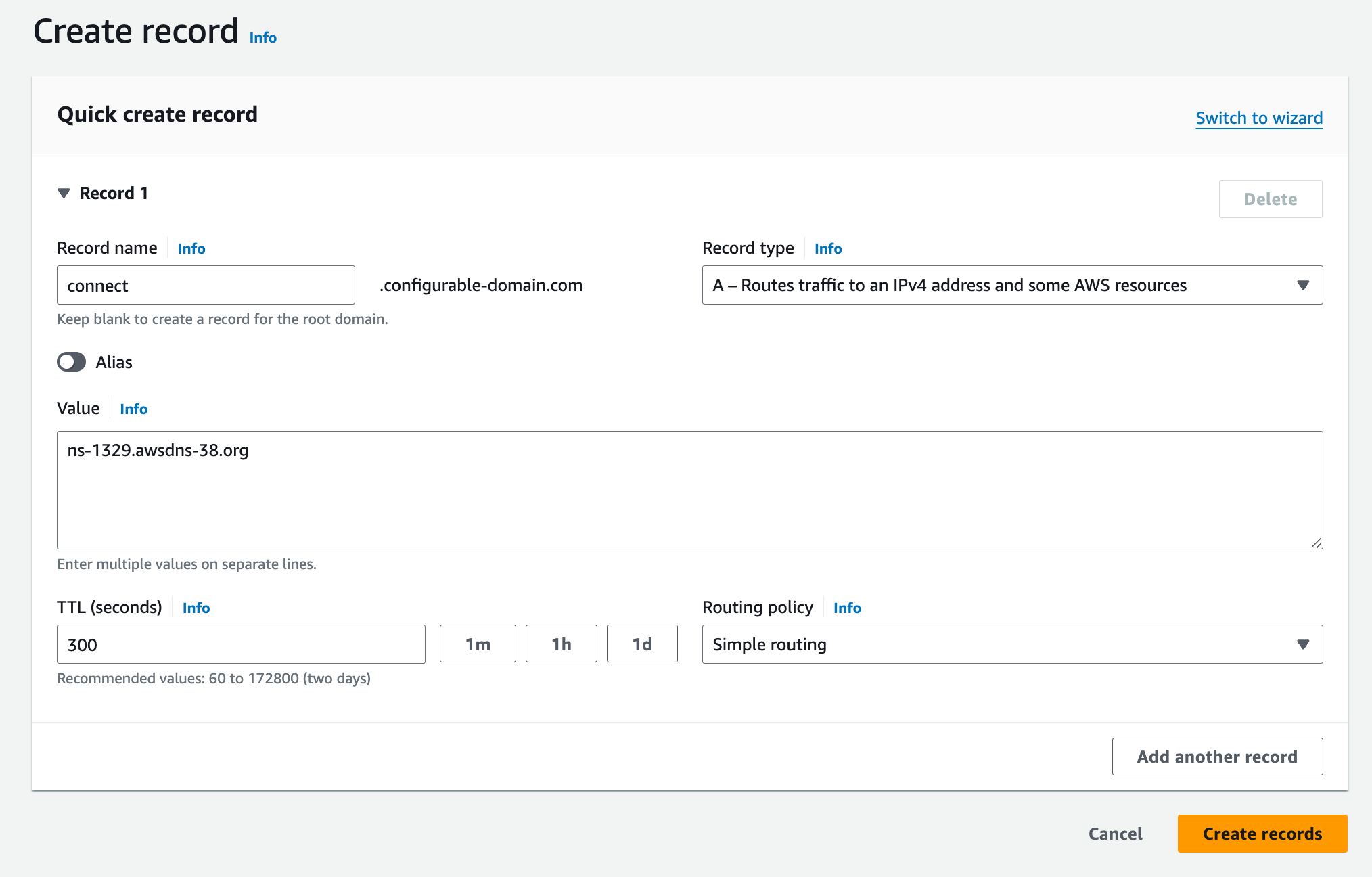
You should have four new records when you’re done.
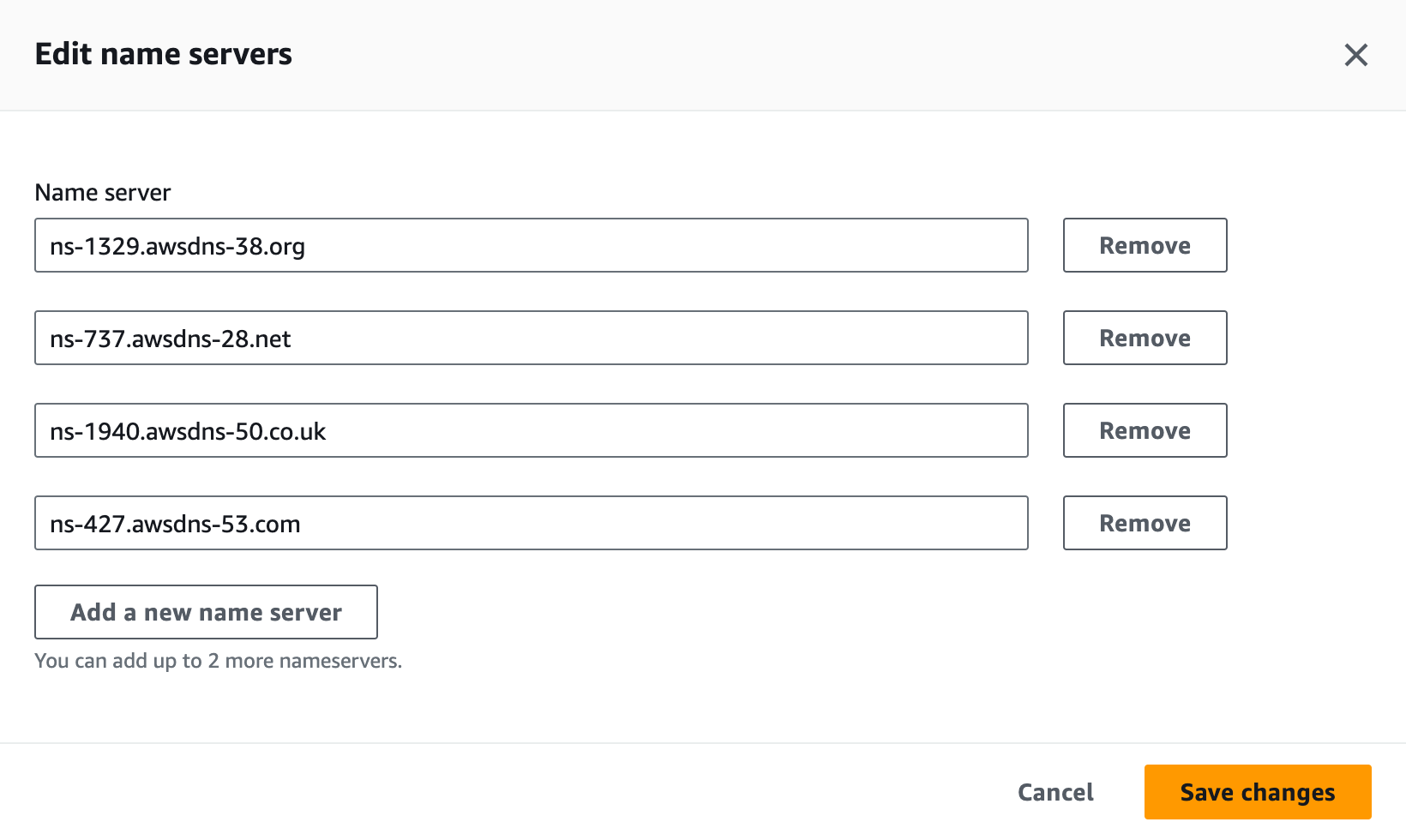
You can run the following command to get the values you need if you didn't save the response.
Loading…
Create a custom wildcard domain
Next, create a custom wildcard domain, which will allow you to create endpoints and receive traffic on any subdomain of your domain.
For example, you might create *.customer1.{YOUR_DOMAIN}. You would then be able to create endpoints
on app.customer1.{YOUR_DOMAIN} and dev.customer1.{YOUR_DOMAIN}. It can be helpful to create
a separate subdomain for each customer site you wish to connect to.
Run the following command, substituting your API key for {API_KEY} and your domain for {YOUR_DOMAIN}:
Loading…
You should receive a 201 response similar to the following:
Loading…
You'll need values from the response in the next section.
Update DNS records
Next, add two CNAME records to your DNS provider's registry, providing values from the previous response.
First add a CNAME record for the wildcard subdomain you just created.

Then add another record for the
ACME (Automated Certificate Management Environment)
validation. For the record, enter _acme-challenge.{SUBDOMAIN}, and use the value of the acme_challenge_cname_target property from from previous response for the value. For the example above, the record name would be
_acme-challenge.customer1.
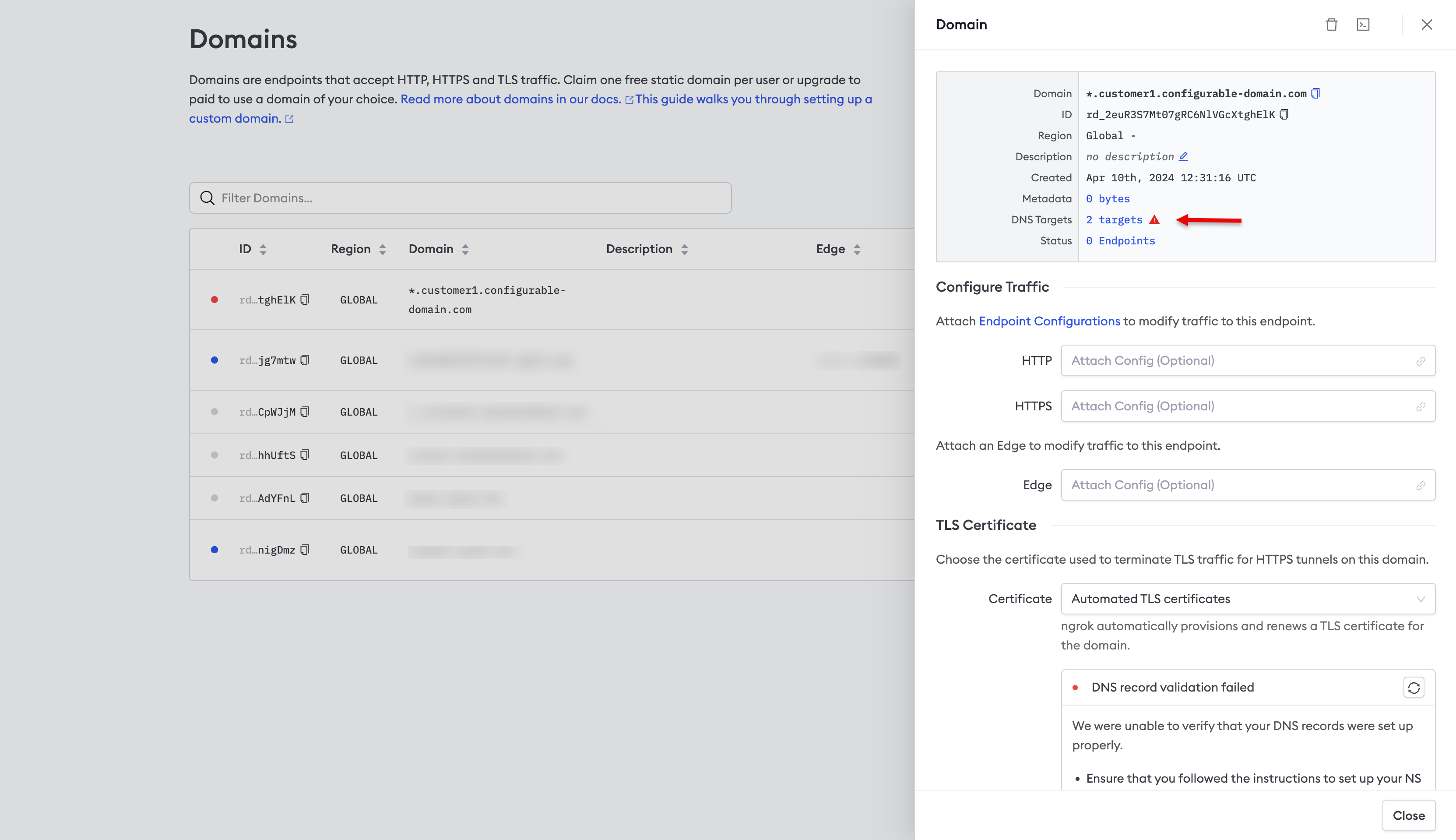
Verify DNS
Use the ngrok dashboard to verify that you’ve configured DNS correctly.
- Login to the ngrok dashboard.
- Click Domains in the left-hand navigation menu.
- Click on your wildcard domain under Domain.
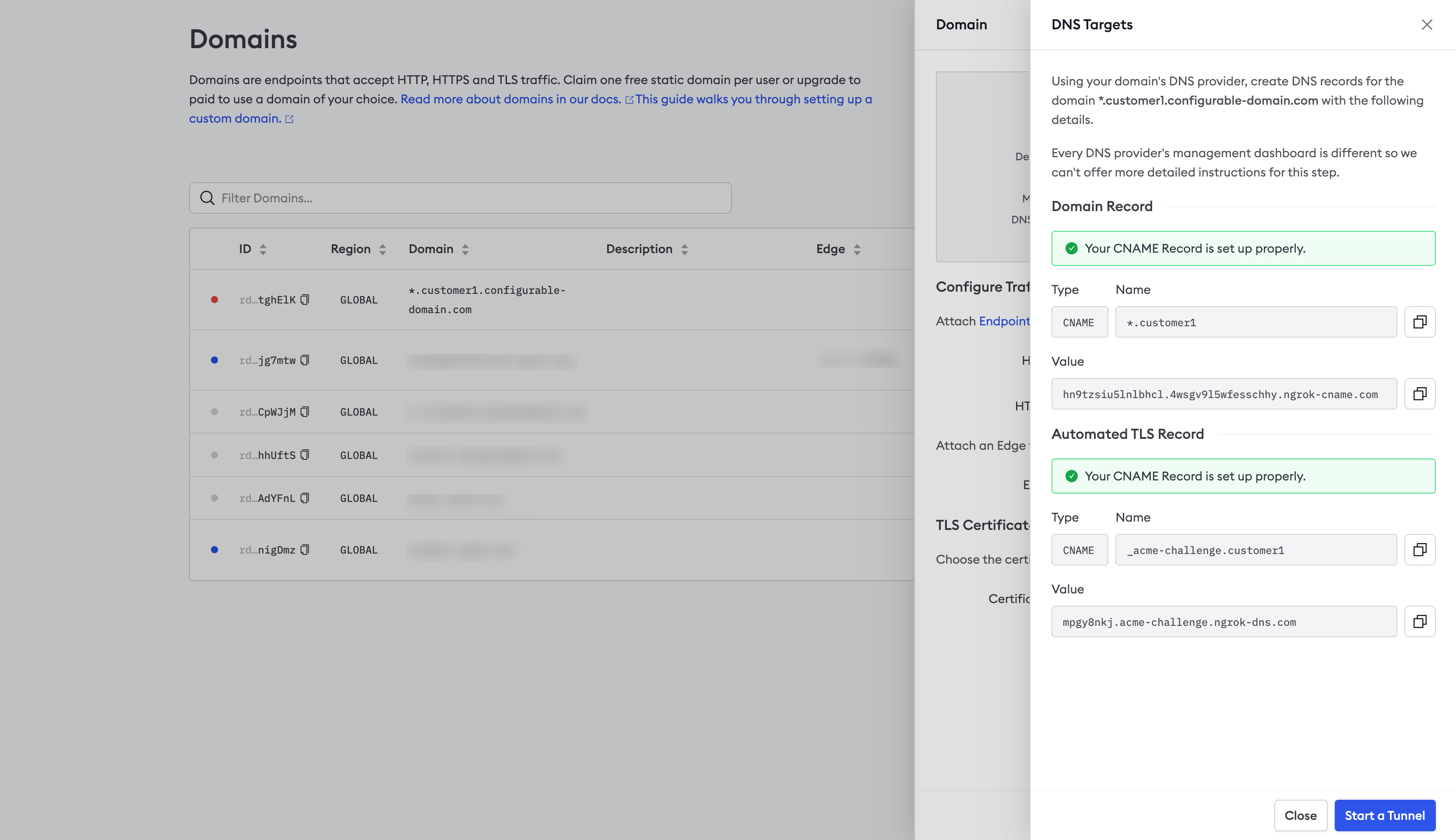
- Click 2 targets next to DNS Targets in the panel displayed on the right-hand side of the screen, as denoted by the arrow in the screenshot below.
- Click Check Status, as denoted by the arrow in the screenshot below.
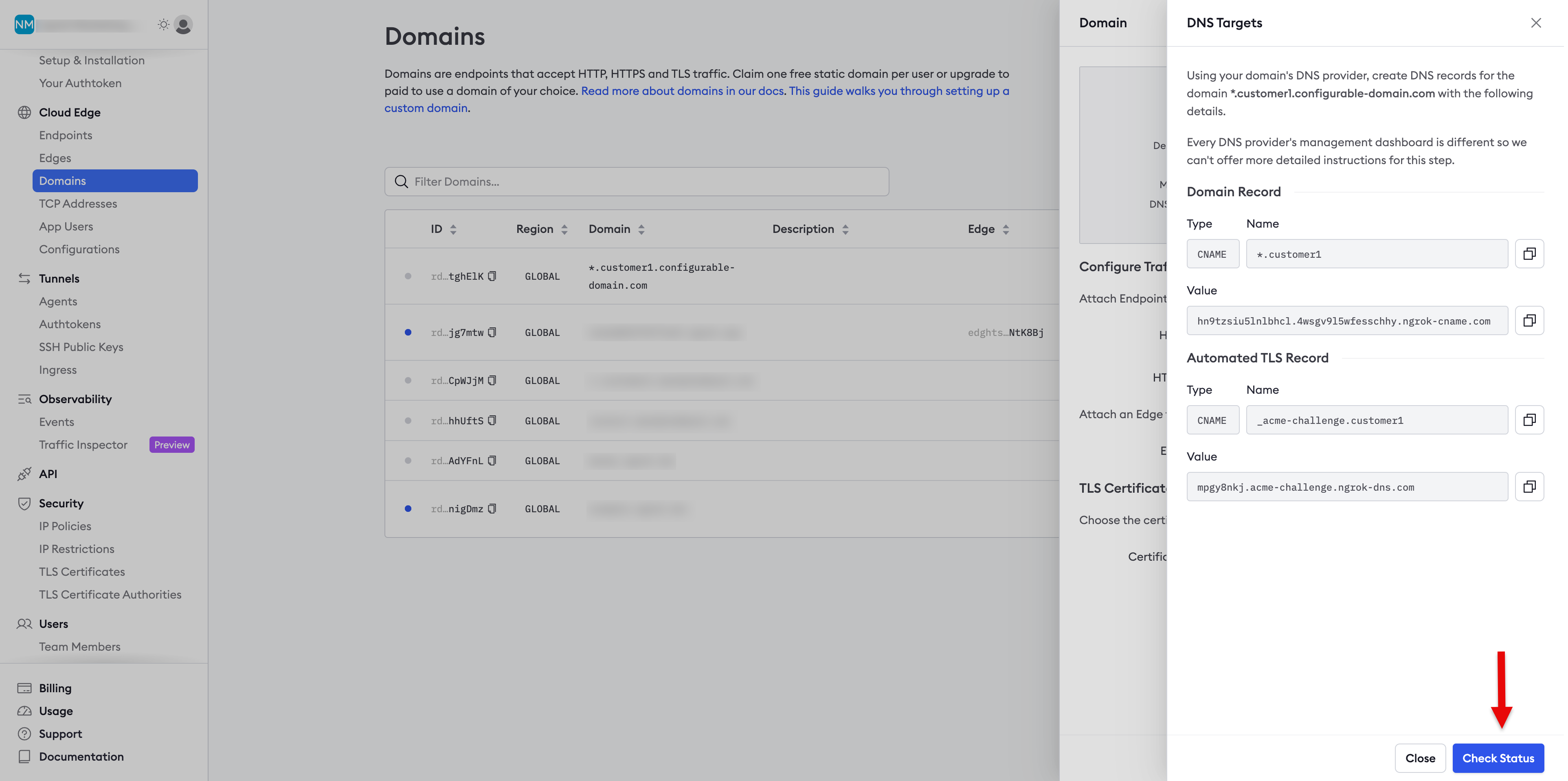
- You should see a successful response similar to the screenshot below.
Create a bot user
Now, you’ll create a bot user so that in the next section, you can create an agent authtoken independent of any user account. A bot user does not belong to a particular user account. Run the following command to create a new bot user, providing your API key and a description:
Loading…
You should receive a 201 response similar to the following:
Loading…
Create the agent authtoken
You should start each agent using a separate authtoken, and that token should belong to a bot user.
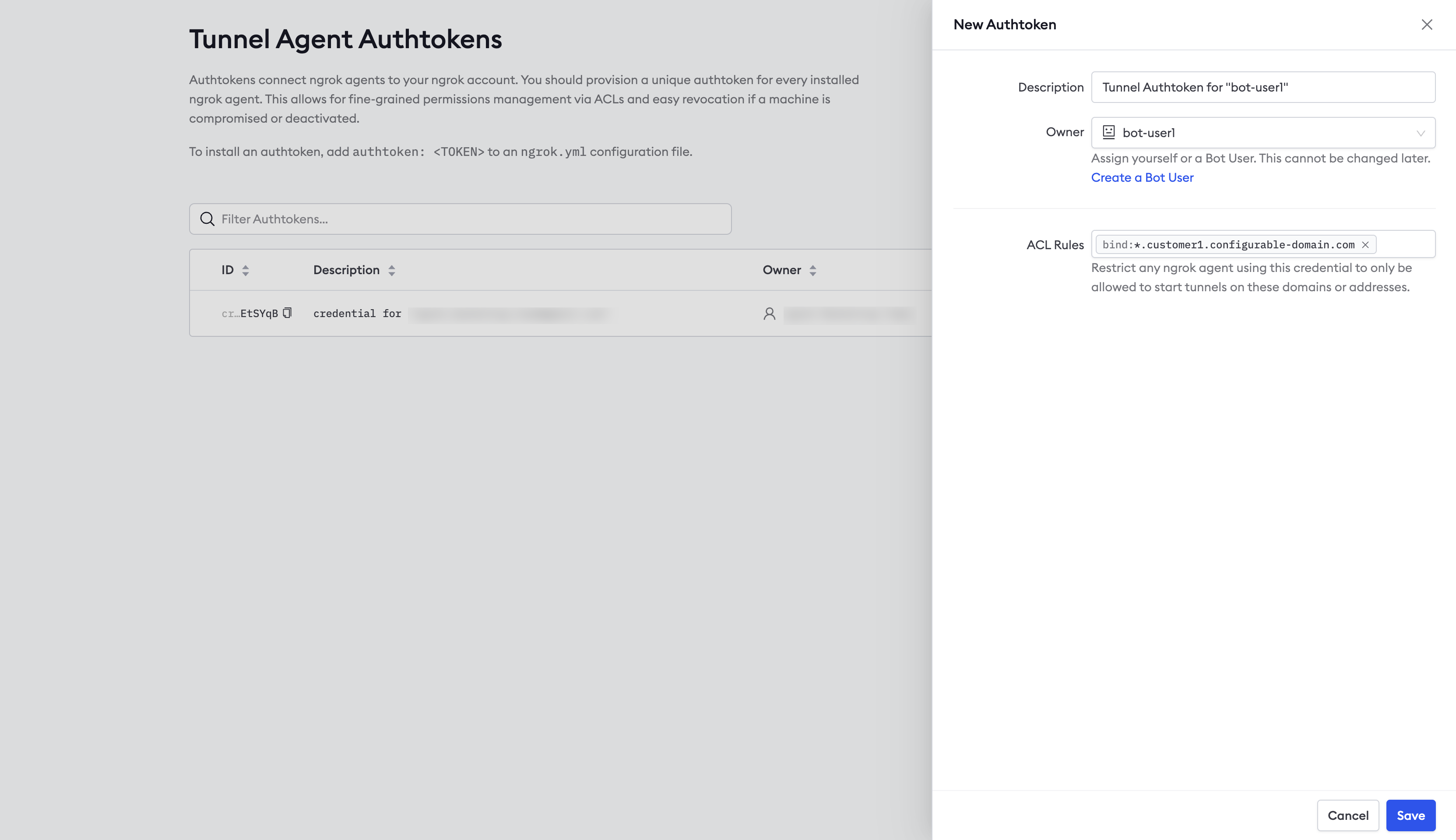
To create an authtoken, login to the ngrok dashboard and click Authtokens
under Tunnels, then click Add a Tunnel Authtoken.
For Owner, select the bot user you use created, and select bind:*.customer1.{YOUR_DOMAIN} for the ACL Rules.
This ACL will allow an agent with the authtoken to create tunnels on any subdomain of customer1.{YOUR_DOMAIN}.
Configure the ngrok agent API
You can use the ngrok agent API to start and stop tunnels remotely, collect and replay captured requests, and collect stats and metrics.
The API runs on localhost:4040 wherever the agent runs, but you can start an ngrok tunnel to make the API available
remotely.
Please note that tunnels started with the agent API do not persist in the event of an agent restart or network outage.
Update ngrok.yml
Create a tunnel definition in the ngrok.yml config file. You can then run the ngrok agent and start and stop tunnels as needed using the ngrok agent API.
You'll need to modify the ngrok.yml config file before running the agent. You can modify the file that resides in the default location:
- Linux:
~/.config/ngrok/ngrok.yml - MacOS (Darwin):
~/Library/Application Support/ngrok/ngrok.yml - Windows:
%HOMEPATH%\AppData\Local\ngrok\ngrok.yml
Rather than edit the default ngrok.yml config file, you can provide your customer with a separate config file.
This keeps your config separate from their existing ngrok.yml config file. You can then pass it as an argument when
you run the ngrok agent. ngrok merges all config files, and you won't need to modify your customer's config file.
This is useful when your customer already uses ngrok and you wish to use the existing
agent to serve the ngrok agent API.
Refer to the region_domain values you saved when you created the custom agent ingress address.
These are custom addresses for ngrok’s global Points of Presence (POPs).
Support for Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB)
is not yet available when using a custom agent ingress address, so you’ll
need to specify the POP this agent should use to connect to the ngrok platform.
Add the following sections to the ngrok.yml config file, substituting the appropriate values for your environment,
including a subdomain to connect to the agent api, such as agent.customer1.configurable-domain.com:
Loading…
Start the agent to access the agent API
Now that you’ve updated the ngrok.yml config file, start the tunnel for the agent API by running the following
command wherever you installed the agent:
ngrok start agent-api
Note that “agent-api” is the name given to the tunnel in the ngrok.yml example config file. You can use any descriptive
name for this tunnel. In this case, you’re starting a tunnel to serve the ngrok agent API on https://agent.customer1.{YOUR_DOMAIN}.
If you wish to provide your customer with a custom ngrok.yml config file rather than modifying the one in the default
location, as mentioned previously, you can pass the path to the file when you start the tunnel:
ngrok start agent-api –config /path/to/ngrok.yml
You can pass multiple paths to config files, and ngrok will merge them before starting.
Start tunnels in your customer’s network
You now have the ngrok agent running in your customer's environment and can use the agent API to start and stop the tunnels necessary to access your customer’s APIs.
To start a tunnel to connect to your customer’s API, run the following command, substituting the appropriate values for your environment:
Loading…
The example below creates a tunnel on port 3000 and serves it at api.customer1.configurable-domain.com.
Because a previous step created the wildcard domain on *.customer1.configurable-domain.com, a tunnel can be started on
api.customer1.configurable-domain.com without reserving that subdomain.
Loading…
Add mutual TLS (mTLS)
At this point, you can access APIs running at the external site, but the connection is unencrypted. Next you'll add mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication to the tunnel to allow ngrok to verify the identity of the client and server.
When you start the tunnel, you can send additional properties in the payload to provide the certificate authority (CA) private key, the signed server certificate, and the server’s private key.
If you previously started a tunnel, stop it now. Then, to start a fully encrypted tunnel with mTLS, run the following command, replacing the variables with the appropriate values for your environment:
Loading…
Generate test certificates
The script below generates tests certificates, which may be useful during implementation or proof of concept. You should provide certificates signed by an official Certificate Authority when running tunnels in production.
To generate certificates for testing, run the script below, substituting your wildcard domain for {YOUR_WILDCARD_DOMAIN}.
For the example above, you'd use *.customer1.configurable-domain.com.
Loading…
When the script completes, you should have the following new files:
- ca-crt.pem
- ca-crt.srl
- ca-key.pem
- client-crt.pem
- client-csr.pem
- client-key.pem
- server-crt.pem
- server-csr.pem
- server-key.pem
Some of these are intermediary files you can ignore.
Run the command below from the same directory where you generated the certificate files to
start a fully encrypted tunnel, substituting your domain for {YOUR_DOMAIN} and supplying a value
for {PORT}:
Loading…
Please note that these certificates should be used for testing purposes only. You should obtain certificates signed by a Certificate Authority for use in production.
Access APIs in external site
You now have connectivity to your customer’s external site and can access any endpoint of the API running on the port you provided in the previous step. You’ll pass the client certificate in each request to the API, and ngrok will terminate TLS in our global network. ngrok will only forward the request to your customer’s network if it includes a valid client certificate signed by a Certificate Authority that you’ve added to your ngrok account.
You can access your customer’s API using curl, passing the certificates:
Loading…
Note that curl will return an error if you pass a self-signed certificate. If you’re using self-signed certificates during implementation, you can use Postman to connect to your customer’s API.
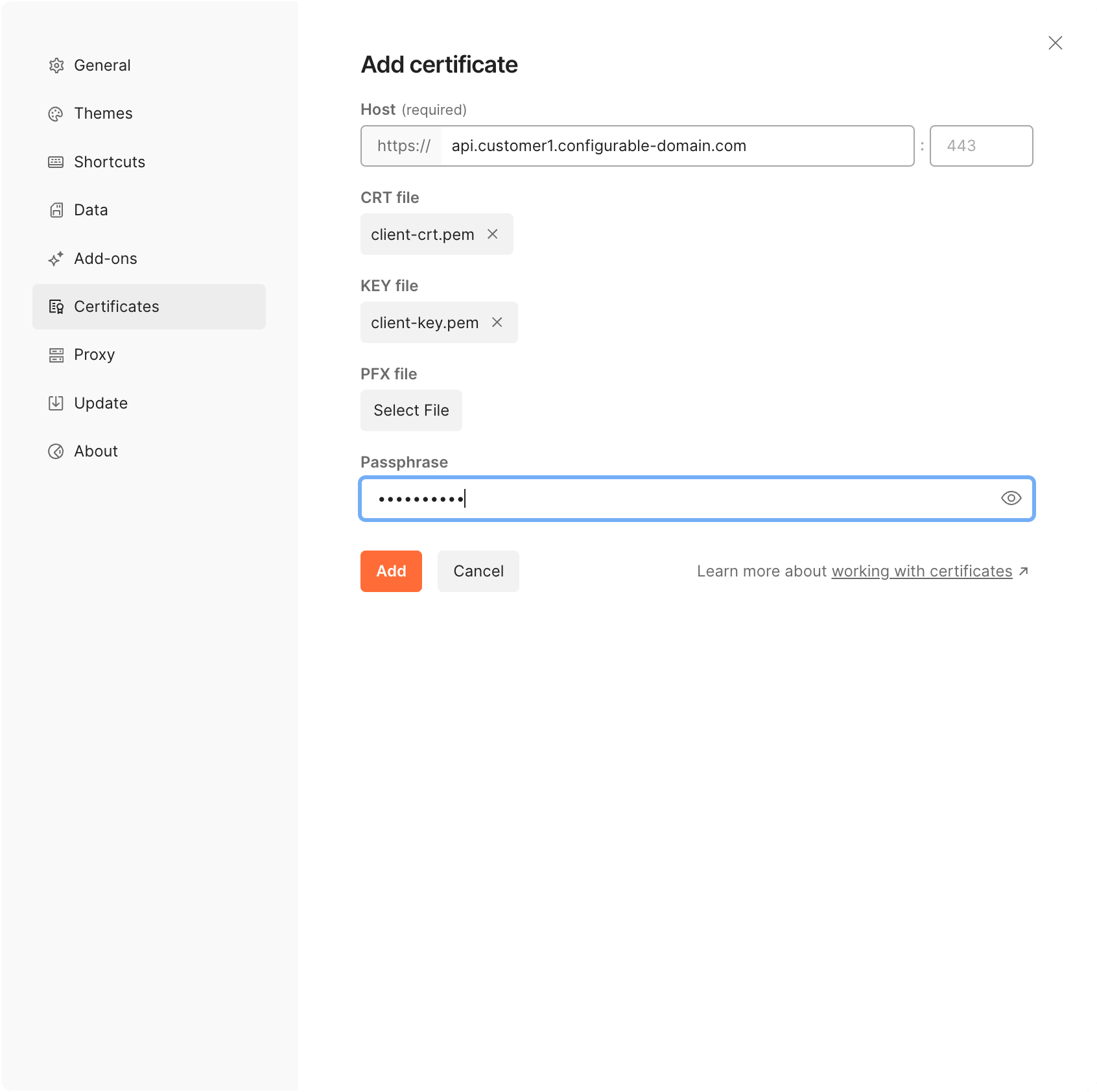
To add a certificate to Postman:
- Select Settings under Postman in the top menu.
- Click Certificates in the left-hand navigation bar.
- Click Add Certificate.
- Enter the subdomain you configured to access your customer’s API, but do not include an endpoint, for Host. For example,
api.customer1.configurable-domain.comfor the previous example. - Add the client certificate for CRT file.
- Add the client key for Key file.
- Enter a Passphrase if you set one when you created the client certificate.
- Click Add to save the files to your account.
You can now use Postman to make requests to your customer’s API, and Postman will automatically send the certificates you added whenever you access a URL on the domain. Both the request and the response will be encrypted with TLS, so there’s no need to add any additional security policies.